Understanding Why Your Dog Is Throwing Up Yellow Bile: A Comprehensive Guide
Deciphering the Signs: What Does it Mean When Your Dog is Throwing Up Yellow Bile?
Seeing your beloved dog throwing up yellow bile can be an alarming experience for any pet parent. This specific type of vomit typically signals that your dog's stomach is empty, and they are expelling stomach acid mixed with bile, a phenomenon often referred to as bilious vomiting syndrome. The distinct yellow hue comes from bile itself—a vital digestive fluid skillfully produced in the liver and meticulously stored in the gallbladder. Its primary role is to assist with digestion in the small intestine. When the stomach is devoid of food, bile can regrettably reflux back into the stomach, leading to its expulsion.
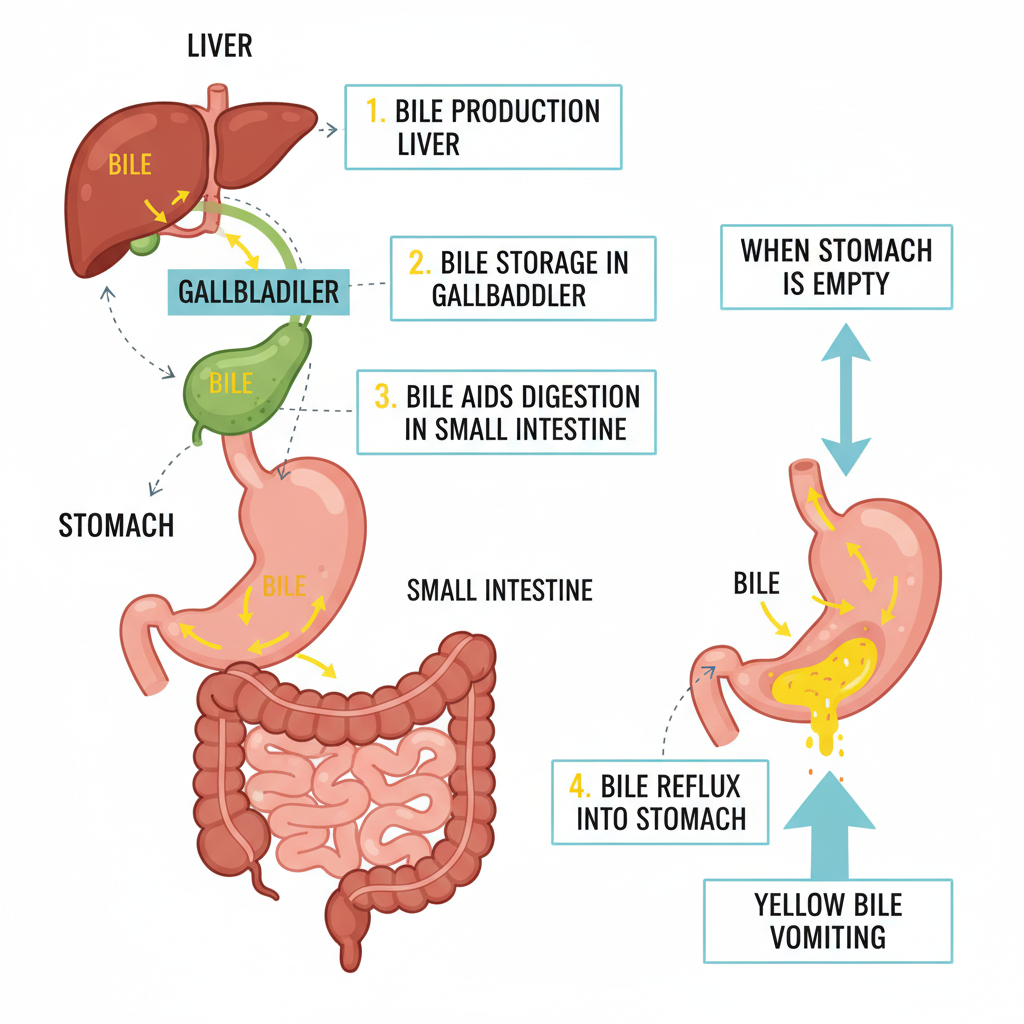
While an isolated incident of a dog throwing up yellow bile might not immediately warrant serious concern, its frequent occurrence or presence alongside other distressing symptoms could be a critical indicator of an underlying health issue. At Petscarelab, we always recommend vigilant monitoring of your canine companion. If your dog exhibits frequent episodes, appears unwell, or displays any additional concerning signs, prompt consultation with a trusted veterinary professional is paramount.
Unpacking the Causes: Why Your Dog Might Be Throwing Up Yellow Bile
There are several compelling reasons why a dog might unexpectedly be throwing up yellow bile:
Bilious Vomiting Syndrome (BVS): A Common Reason for Yellow Bile Vomit in Dogs
Bilious Vomiting Syndrome, often abbreviated as BVS, stands as one of the most frequent culprits behind a dog throwing up yellow bile. This condition typically manifests during periods of prolonged stomach emptiness, such as early morning or late at night. The irritation to the stomach lining arises from an accumulation of bile and stomach acid, which, without food to absorb it, can become quite abrasive.
Management Strategies:
- Optimizing Feeding Schedules: Transitioning to smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can help keep the stomach from becoming overly empty.
- The Power of a Bedtime Snack: A small, easily digestible snack given before bedtime can be remarkably effective in neutralizing stomach acids overnight.
- Veterinary-Prescribed Interventions: In some cases, your veterinarian might recommend specific medications, such as antacids or anti-nausea drugs, to provide relief and protect the stomach lining.
Diet-Related Concerns Leading to Yellow Bile Vomit
The food your dog consumes dramatically influences their digestive health. Dietary indiscretions, such as food allergies, sensitivities, or consuming spoiled items, are frequent triggers for stomach upset and subsequent vomiting, which can present as yellow bile. Additionally, dogs who eat their meals too rapidly may inadvertently swallow air, contributing to gastric irritation.
Remedial Actions:
- Temporary Bland Diet: For acute episodes, introducing a bland, easily digestible diet—such as plain boiled chicken and rice—for a few days can help soothe an irritated stomach.
- Professional Dietary Consultation: If you suspect food allergies or sensitivities are at play, our experts at Petscarelab strongly advise a detailed discussion with your veterinarian to explore potential dietary changes and specialized food options.
Gastrointestinal Disorders That Cause Your Dog to Throw Up Yellow Bile
More persistent or chronic instances of a dog throwing up yellow bile can sometimes point towards underlying gastrointestinal disorders. Conditions such as Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), pancreatitis, or gastric ulcers can severely disrupt the digestive system, leading to recurrent nausea and the expulsion of bile.
Veterinary Approaches:
- Targeted Medication: Treatment protocols are highly specific, based on the precise diagnosis, and may involve a range of medications.
- Specialized Dietary Management: Tailored dietary modifications are often a cornerstone of managing these conditions.
- Surgical Intervention: In more severe or complicated cases, surgical procedures might be necessary to address the root cause.
Systemic Illnesses and Their Connection to Bile Vomiting
Beyond the digestive tract, systemic illnesses impacting other major organ systems can also lead to a dog throwing up yellow bile. Chronic conditions like kidney disease, liver disease, or even diabetes can trigger pervasive nausea and vomiting as their effects ripple throughout the body.
Management Focus:
- Addressing the Primary Illness: The core of treatment lies in diligently managing and addressing the underlying systemic disease.
- Supportive Symptom Care: Concurrently, supportive care is crucial, focusing on alleviating nausea and preventing or treating dehydration to ensure your dog's comfort and recovery.
Dangerous Ingestion: Toxins or Foreign Objects
Curiosity can sometimes lead our canine companions into dangerous situations. If your dog ingests something toxic, such as certain plants or household chemicals, or an indigestible foreign object like a piece of a toy or a sock, it can lead to severe gastrointestinal irritation or even a life-threatening blockage, resulting in immediate and forceful vomiting, including yellow bile.

Emergency Interventions:
- Induced Vomiting: Under strict veterinary guidance, inducing vomiting may be considered for certain toxins, though this should never be attempted at home without professional advice.
- Activated Charcoal: For ingested toxins, activated charcoal can be administered to absorb harmful substances and prevent their absorption into the bloodstream.
- Advanced Procedures: For foreign objects causing blockages, endoscopy (a minimally invasive procedure using a camera) or surgery may be required to safely remove the obstruction.
Intestinal Parasites: An Often-Overlooked Cause
Unwanted guests within the digestive system, such as intestinal parasites like roundworms or hookworms, can cause significant irritation to the gastrointestinal tract. This irritation can manifest as various symptoms, including nausea and the expulsion of yellow bile.
Effective Treatment:
- Targeted Deworming: A veterinarian will prescribe specific deworming medication designed to eliminate these internal parasites, bringing relief and restoring digestive health.
The Impact of Stress and Anxiety on Canine Digestion
Our dogs, much like us, can experience profound emotional stress and anxiety. For some sensitive canines, these psychological pressures can manifest physically, leading to gastrointestinal upset and even vomiting, which may include yellow bile.
Holistic Management:
- Identifying Stressors: The first step is to carefully identify and, if possible, eliminate or mitigate the sources of stress in your dog's environment.
- Behavioral Support: Implementing positive reinforcement behavioral training strategies can help manage anxiety. In more severe cases, your veterinarian or a veterinary behaviorist might recommend anxiety-reducing medications to support your dog's emotional well-being.
When to Seek Urgent Veterinary Care for Your Dog Throwing Up Yellow Bile
While an isolated instance of your dog throwing up yellow bile might not always signal an immediate crisis, certain circumstances undeniably warrant prompt and decisive action by contacting your veterinarian. Ignoring these red flags could potentially endanger your beloved companion.
Consider veterinary consultation immediately if:
- Persistent or Frequent Episodes: Your dog is vomiting bile multiple times within a single day or if the vomiting persists for more than 24 hours.
- Accompanying Alarming Symptoms: The vomiting is coupled with other distressing signs such as profound lethargy, persistent diarrhea, a complete loss of appetite, obvious abdominal pain, an elevated fever, or, critically, any presence of blood in their stools.
- Indications of Dehydration: Observe for classic signs of dehydration, including sunken eyes, unusually dry or tacky gums, or a noticeable decrease in skin elasticity (when gently pinched, the skin remains tented).
- Recurring or Chronic Episodes: Your dog exhibits a recurring pattern of vomiting yellow bile over an extended duration, suggesting an underlying chronic issue.
- Vulnerable Age Groups: Puppies and senior dogs are inherently more susceptible to rapid dehydration and serious complications from underlying health problems, making immediate attention crucial.
- Pre-existing Health Conditions: Your dog has a known medical condition, such as diabetes or kidney disease, which can be significantly exacerbated by vomiting.
- Suspected Dangerous Ingestion: You have reason to believe your dog may have ingested something toxic or a foreign object, requiring urgent assessment and intervention.
What to Expect When Your Vet Addresses Your Dog Throwing Up Yellow Bile
When you bring your dog to the veterinary clinic concerning instances of a dog throwing up yellow bile, rest assured that your veterinary team will conduct a meticulous investigation to uncover the root cause. This typically involves a comprehensive examination alongside a series of targeted diagnostic tests.
The Thorough Physical Examination
Your veterinarian will begin by carefully assessing your dog's overall physical condition, checking vital signs, evaluating hydration levels, taking their temperature, and gently palpating their abdomen for any signs of pain, distention, or abnormalities.
Detailed History Gathering
To gain crucial insights, the vet will ask you a series of pertinent questions. Being prepared with detailed answers will greatly assist in the diagnostic process. You might be asked about:
- The frequency and duration of your dog's vomiting episodes.
- When the symptoms first appeared and any noticeable patterns.
- Any other accompanying symptoms or changes in behavior.
- Recent changes in your dog's diet, routine, or environment.
- Your dog's complete medical history and any current medications they are receiving.
Advanced Diagnostic Tests
Depending on the initial findings, your veterinarian may recommend one or more of the following diagnostic procedures:
- Comprehensive Blood Work: This includes a Complete Blood Count (CBC) and a chemistry panel, which can reveal signs of infection, inflammation, assess vital organ function (kidney, liver), and detect metabolic imbalances.
- Urinalysis: A urine sample can provide critical information about kidney function, hydration status, and help rule out urinary tract infections or other systemic conditions.
- Fecal Examination: A stool sample will be analyzed to screen for the presence of intestinal parasites that could be irritating the digestive system.
- X-rays (Radiographs): These imaging scans are invaluable for detecting foreign objects, identifying potential tumors, or observing signs of organ enlargement within the abdominal cavity.
- Abdominal Ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging technique offers detailed, real-time views of internal organs, providing a closer look at the stomach, intestines, pancreas, and liver for subtle abnormalities.
- Endoscopy: In specific cases, a flexible camera (endoscope) may be gently guided into the esophagus and stomach to visually inspect the lining for ulcers, inflammation, or foreign bodies, and to collect tissue biopsies if needed.
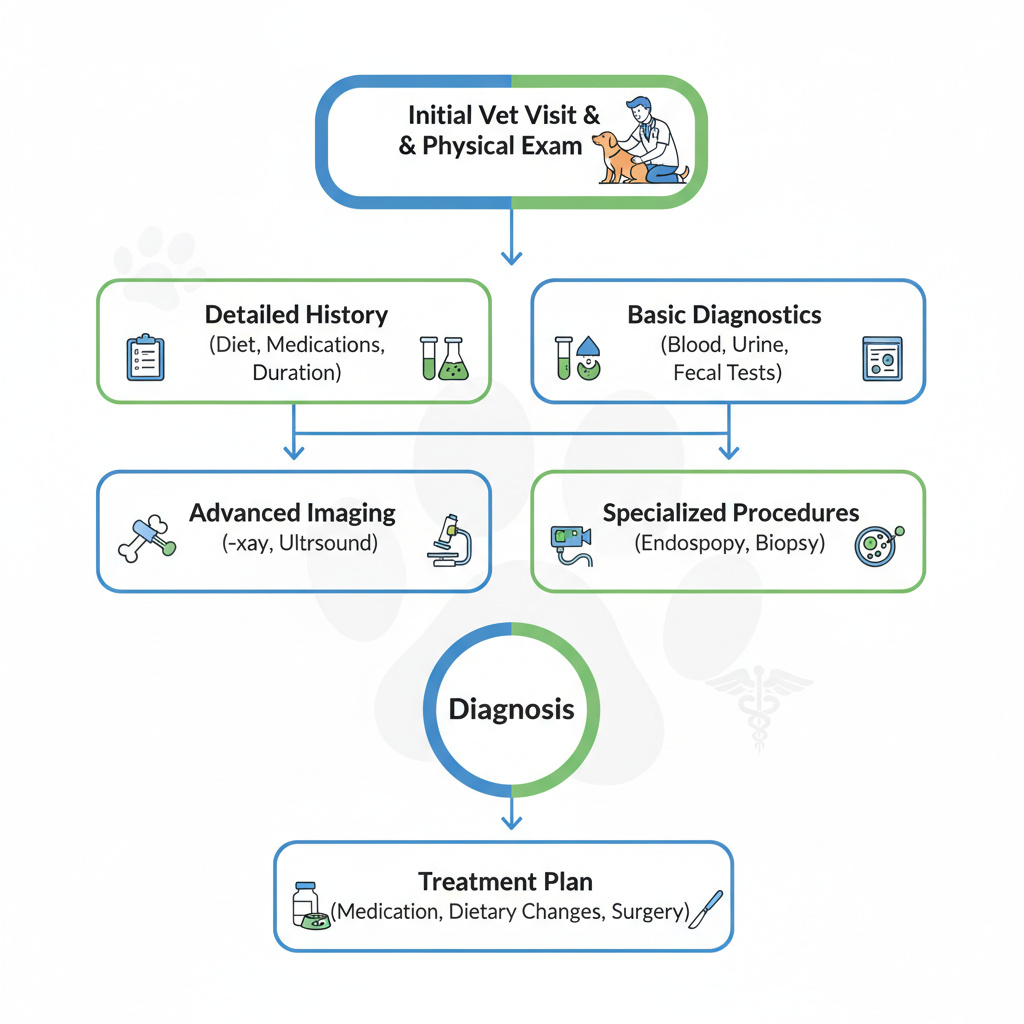
Tailored Treatment Protocols
The treatment plan will be precisely customized based on the identified underlying cause of your dog's condition:
- Fluid Therapy: To combat or prevent dehydration, intravenous (IV) or subcutaneous fluids will often be administered to replenish essential electrolytes and maintain hydration.
- Anti-Nausea Medications: Medications such as maropitant or ondansetron can be highly effective in reducing nausea and stopping the cycle of vomiting.
- Gastric Protectants: Drugs like famotidine or omeprazole may be prescribed to reduce stomach acid production and protect the delicate lining of the stomach.
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection is diagnosed as the cause, a targeted course of antibiotics will be initiated.
- Deworming Protocols: Should parasites be identified, appropriate deworming medication will be administered.
- Specialized Dietary Interventions: Your vet might recommend prescription diets specifically formulated for sensitive stomachs, managing food allergies, or supporting particular organ diseases.
- Surgical Solutions: For serious issues like intestinal blockages caused by foreign objects or the presence of tumors, surgical intervention may be the necessary course of action.
At Petscarelab, we strongly emphasize the importance of meticulously following your veterinarian's comprehensive advice and completing the full course of any prescribed medications to ensure your dog's optimal recovery and long-term health.
Proactive Steps: Preventing Your Dog From Throwing Up Yellow Bile
While it's impossible to entirely eliminate every potential cause for your dog throwing up yellow bile, conscientious pet parents can implement a variety of proactive strategies to significantly reduce its occurrence and promote overall digestive wellness.
Consider these essential preventative measures:
- Establish a Consistent Feeding Routine: For dogs susceptible to bilious vomiting syndrome, transitioning to smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can prevent the stomach from remaining empty for too long. A light, easily digestible snack before bedtime can also be highly beneficial.
- Prioritize a Premium, Balanced Diet: Ensure your dog receives a high-quality, nutritionally complete dog food that is specifically formulated for their age, breed, and activity level. Avoid abrupt and frequent changes to their diet, which can upset their digestive system.
- Strictly Limit Table Scraps: Many human foods are not only inappropriate but can be outright toxic or cause severe gastrointestinal upset in dogs, leading to vomiting.
- Deter Scavenging and Ingestion of Harmful Items: Be vigilant about preventing your dog from accessing garbage, consuming spoiled food, or ingesting foreign objects. Always keep household toxins, medications, and hazardous plants well out of their reach.
- Maintain Robust Parasite Control: Adhere to your veterinarian's recommendations for regular deworming and year-round flea and tick prevention to protect your dog from internal and external parasites that can cause digestive distress.
- Cultivate a Low-Stress Environment: Recognize and minimize stressors in your dog's daily life, as emotional anxiety can manifest as physical symptoms, including stomach upset.
- Ensure Constant Access to Fresh Water: Adequate hydration is paramount for digestive health. Always provide your dog with ample fresh, clean water throughout the day.
- Schedule Routine Veterinary Check-ups: Regular preventive veterinary examinations are crucial for early detection of potential underlying health issues before they escalate into more serious problems, like chronic vomiting.
- Utilize Slow Feeder Bowls: If your dog tends to eat too quickly, a slow feeder bowl can significantly slow down their mealtime, reducing the amount of air they gulp and thereby lessening the likelihood of stomach upset and subsequent vomiting.







